The performance of five-axis CNC machining centers has now reached an advanced level, being widely used in fields such as medical devices, new energy vehicles, semiconductors, precision molds, aerospace, and more. Moreover, the industry continues to grow year after year. So what exactly is 5-axis machining, what are the axes, and what are its advantages, and differences compared to 3-axis and 3+2 machining?
What is 5-Axis Machining?
CNC machining is a manufacturing method that removes material using cutting tools on different machines like mills, lathes, and machining centers. 5-axis CNC machining is a type of CNC machining, in the process, the part and cutter can move along all five axes, usually used to machine complex parts or components that require high precision. What makes 5-axis machines different is the addition of tilt and rotation capabilities to the workpiece fixture or tool spindle itself. With a fifth axis, operators need only one setup to machine up to five surfaces, making the process both highly accurate and efficient.
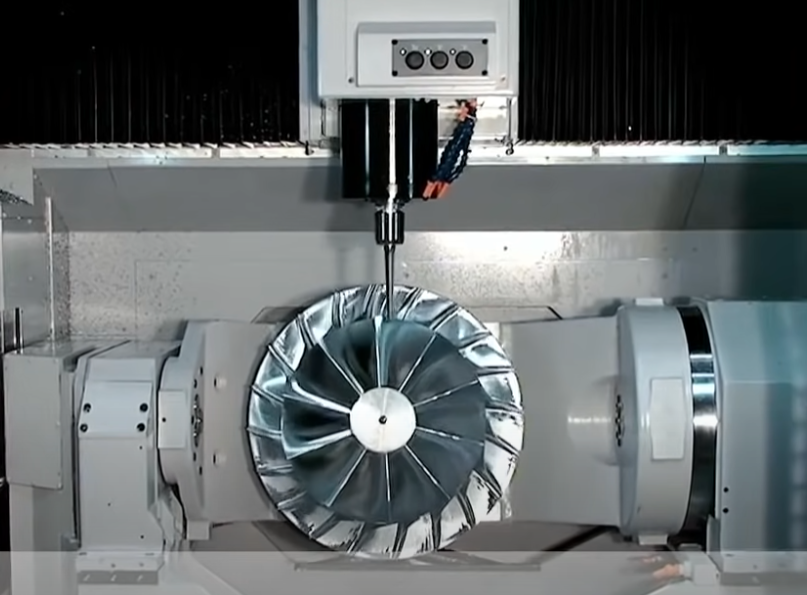
What does the 5-axis mean?
5-axis machines have two more axes than the more common 3-axis machines. Five axes mean the cutting tool can contact the workpiece from five directions instead of three, so more movement at one time becomes available. When using a three-axis machine tool, the tool can move along the X and Y axes while using the Z axis for up and down movement. With five-axis machining, users gain two additional rotary axes from three axes defined as A, B, and C, where A rotates around the X axis, B rotates around the Y axis, and C rotates around the Z axis. The specific configuration of a 5-axis machining center determines which two of the three rotary axes it uses, which can have any combination of AB, AC, or BC configurations, relating to the type of five-axis machine. Additionally, in vertical machining centers the X and Y axes lie in a horizontal plane while the Z axis lies in a vertical plane; in horizontal machining centers the Z and Y axes are opposite.
Advantages of 5-Axis Machining
– Complex geometries: 5-axis machining can handle very complex part shapes and surfaces, such as those found in aerospace, medical, and automotive components. It allows machining from multiple angles to easily realize complex designs.
– High accuracy and better surface finish: Since the tool can contact the workpiece from different angles, five-axis machining typically provides higher accuracy and a better surface finish, reducing later polishing and finishing work.
– Reduced machining time: 5-axis machining can complete multiple faces or features in a single fixture setup, reducing part re-fixturing and improving efficiency and cycle time.
– Increased tool life: By positioning the tool at optimum angles to the workpiece, wear on the tool can be reduced, extending tool life and lowering production costs.
– Automation and flexibility: Modern five-axis machining centers often feature automated capabilities allowing flexibility for small-batch production and rapid changes in production demand.
– Reduced human error: Due to computer control of machining processes, reliance on human operation is reduced, lowering the possibility of human error and improving the consistency and reliability of machining.
– Strong adaptability: Five-axis machines can be used for machining a variety of materials, like metals, plastics, and composites, with strong adaptability to satisfy different industrial fields’ demands.
Differences Between 5-Axis and 3-Axis Machining
1) Axes and working area
3-axis machining moves along the X, Y, and Z axes, and 4-axis adds rotation around one of these, allowing the cutting tool to reach more areas of the workpiece.
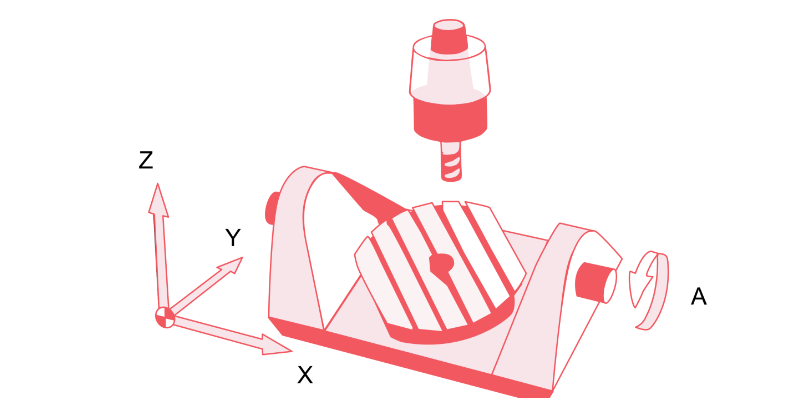
While 5-axis machines have two additional rotary axes for tilting and rotating the part. This allows the cutting tool to approach and enter the part from any direction.
2) Machining efficiency
The limited capabilities of 3-axis machining and increased difficulty ultimately mean lower productivity. When a part requires frequent repositioning or multiple setups to complete all features, actual material removal will take more time. Five-axis CNC machine tools intrinsically minimize multiple setups and tool changes through their multi-axial motions. This streamlines manufacturing processes, improves efficiency, and shortens production timelines. The machine can handle complex tasks in a single setup, reducing downtime and boosting overall production.
3) Capabilities
5-axis machines allow designs that are difficult or impossible to machine with 3-axis, enabling innovative automotive, medical, energy, and other technology products. Their precision benefits industries where details differentiate performance.
4) Innovation in design
Five-axis enables more design possibilities, allowing engineers to conceive advanced tech products previously difficult for the 3-axis.
5) Production line configuration
In terms of production line layout, 5-axis machining has higher flexibility, the clamping times can be reduced, which saves time and labor intensity of workers. The machining center can approach the workpiece from any direction, a single clamping can complete the machining of all surfaces except for the mounting surface, this will improve the accuracy and surface finish. In 3-axis machining, some parts that require the use of long or special cutting tools can often be machined with ordinary tools through rotation and tilting in 5-axis machining. In particular, the protrusion of the tool can be minimized, resulting in more stable machining.
5 Axis vs 3+2 Axis Machining, What Are the Differences?
Both 5-axis and 3+2 machining have their advantages and disadvantages.
1) Setup
The 5-axis has a full 5-axis design that allows movement in all 5 axes simultaneously. 3+2 uses a 3-axis CNC with tilt/rotate tables or trunnions to add 2 additional rotational axes.
2) Types of parts/industries
3+2 is mainly for planar parts. The 5-axis machine can handle more complex contours and is used in industries like aerospace.
3) Capabilities
The 5-axis can machine 5 surfaces simultaneously. 3+2 requires repositioning/index for additional surfaces.
4) Accuracy/precision
5 Axis allows tangential toolpaths for higher precision. 3+2 needs tool repositioning which reduces accuracy.
5) Cycle time
5 Axis can machine parts in a single setup, reducing cycle times. 3+2 requires multiple setups/index which increases cycle time.
6) Surface finish
5 Axis keeps the tool aligned for better surface finishes. 3+2 may have more vibration from repositioning degrading finish.
7) Costs
5-axis machines have higher initial costs. 3+2 retrofits existing machines for lower costs.
8) Programming
5 Axis requires more complex programming for 5D movements. 3+2 programming is simpler with fewer rotational axes.