A spring is a mechanical device that stores and releases energy. Springs can be made from a variety of materials, but most commonly they’re made from hardened steel. A spring is typically formed into the shape of a coil to effectively store and release energy. The most fundamental law relating to springs is Hooke’s Law, which states that the force a spring exerts is proportional to its extension. Spring can be tailored by changing the material or geometry of the spring. This allows engineers to design springs for a wide variety of specific applications.
Types of Springs: Definition, Pros, Cons, Mechanical Properties – CNCJY.com
1. Helical Springs:
Extension Springs
These springs abide by Hooke’s Law, and they have hooks, loops, or other interface geometry at the ends that allow them to be ‘pulled’ and create a resistance force.
- -Pros: They store and absorb energy, as well as create a resistance to a pulling force. They’re often used for trampolines, garage doors, and washing devices.
- -Cons: They can be dangerous when they fail, as they can cause whiplash or other injuries due to the sudden release of stored energy.
- -Price: The price can vary significantly, from less than $1 for small, simple springs, to over $50 for large, custom-made springs.
Torsion Springs
These springs store mechanical energy when they are twisted. When the spring is twisted, it exerts a force in the opposite direction, proportional to the amount it is twisted.
- -Pros: They can store a large amount of energy and are commonly used in clothespins, clipboards, swing-down tailgates, and garage doors.
- -Cons: They require more material and can be more expensive to manufacture. Their failure can result in sudden, unexpected movement of the attached parts.
- -Price: The price can range from $5 for small, simple springs, to over $100 for larger, custom torsion springs.
Compression Springs
These are open-coil helical springs that resist a force applied axially. They are designed to oppose compression and return to their uncompressed length when the applied force is removed.
- -Pros: They are one of the most efficient ways to store energy and can be used in a wide variety of applications, including automotive suspension systems, medical devices, and electronics.
- -Cons: They can buckle under certain conditions, and their efficiency can decrease over time due to wear and tear.
- -Price: The price can range from $1 for small, simple springs, to over $50 for larger, custom compression springs.
Spiral Springs
These are made from a flat strip of metal that is wound into a spiral. They are used in clocks, watches, and other devices that require a constant force.
- -Pros: They provide a constant force over a large range of motion, which is useful in applications like clocks and seatbelts.
- -Cons: Their performance can degrade over time if they are not properly maintained.
- -Price: The price can range from $10 for small, simple springs, to over $100 for larger, custom spiral springs.
2. Leaf Springs:
Elliptical Leaf Spring
These are also known as “full elliptical” springs because they form a complete ellipse. They’re comprised of a central leaf (or main leaf) that has eyes at both ends and additional leaves of decreasing length.
- -Pros: They provide a soft, smooth ride and are durable.
- -Cons: They are large and heavy, which can decrease fuel efficiency.
- -Price: Depending on the size and material, they can range from $100 to $400.
Semi-Elliptical Leaf Spring
These are the most common types of leaf springs and are essentially cut-in-half elliptical leaf springs with one end attached to the vehicle’s frame.
- -Pros: They are simpler and lighter than full elliptical springs.
- -Cons: They provide a harsher ride compared to full elliptical springs.
- -Price: They typically cost between $50 and $200.
Quarter Elliptical Leaf Spring
These are further modifications of the semi-elliptical leaf spring where only a quarter of an elliptical spring is used.
- -Pros: They are light and compact.
- -Cons: They have a lower load capacity compared to full and semi-elliptical springs.
- -Price: They typically cost between $50 and $200.
Three-Quarter Elliptical Leaf Spring
These are a compromise between semi-elliptical and quarter elliptical leaf springs.
- -Pros: They offer a balance between weight, load capacity, and ride comfort.
- -Cons: They are more complex and more expensive to manufacture.
- -Price: They typically cost between $100 and $300.
Transverse Leaf Spring
These are mounted transversely (across) rather than longitudinally (along the length) of the vehicle.
- -Pros: They allow for a lower vehicle height and are lighter in weight.
- -Cons: They provide less lateral stability.
- -Price: They typically cost between $100 and $300.
3. Disk Springs:
Belleville Disk Spring
This is a conical shell that can be loaded along its axis either statically or dynamically.
- -Pros: They have a high load capacity and can be used to dampen vibration and provide a constant load or resist shock impact. They are also useful in applications with space constraints.
- -Cons: They require precise control over their manufacturing process to ensure consistent performance. They also require a higher upfront cost for tooling.
- -Price: They typically cost between $1 and $20 depending on size, quantity, and specific design considerations.
Curved Disk Spring
These springs are curved and can handle larger loads. They’re often used in applications that require a low spring rate and large deflections.
- -Pros: They can handle larger loads and have a larger deflection compared to other disk springs.
- -Cons: They can deform under excessive loads and may not return to their original state.
- -Price: They typically cost between $2 and $25 depending on size, quantity, and specific design considerations.
Slotted Disk Spring
These springs have a slot cut out from their periphery towards the center, allowing them to resist bending stresses.
- -Pros: They offer high resistance to bending stresses and are able to handle larger loads.
- -Cons: They have a limited deflection range and require precision in manufacturing.
- -Price: They typically cost between $5 and $30 depending on size, quantity, and specific design considerations.
Wave Disc Spring
These are pre-stressed flat washers that produce a relatively light load for a small deflection.
- -Pros: They offer light loads, can accommodate larger deflections, and can be used in applications with space constraints.
- -Cons: They have a lower load capacity compared to other types of disk springs and may not be suitable for high-load applications.
- -Price: They typically cost between $0.50 and $15 depending on size, quantity, and specific design considerations.
| Spring Type | Material | Wire Diameter (in) | Coil Diameter (in) | Free Length (in) | Spring Rate (lbs/in) | Maximum Deflection (in) |
| Compression | Music Wire Steel | 0.060 | 0.500 | 1.000 | 30.0 | 0.500 |
| Extension | Beryllium Copper | 0.032 | 0.250 | 1.250 | 12.5 | 0.750 |
| Torsion | Music Wire Steel | 0.032 | N/A | 1.500 | 5.0 | 45 degrees |
| Constant Force | Phosphor Bronze | 0.040 | 0.375 | 1.250 | Gradual 5-15 | 1.000 |
| Push/Pull | Spring Steel | 0.125 | 0.750 | 2.000 | 50.0 | 0.500 |
| Volute | Stainless Steel | N/A | 1.250 | 3.000 | 100.0 | 0.750 |
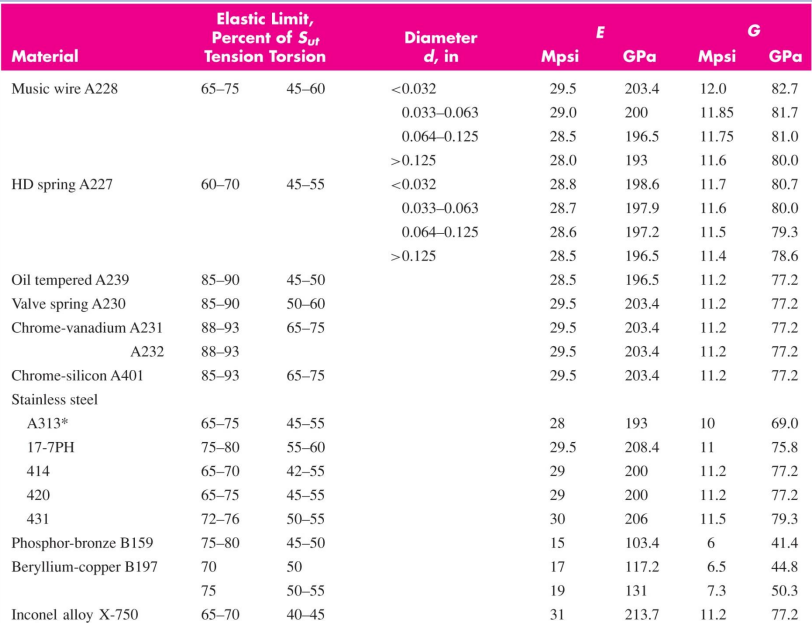
Mechanical Properties of Some Spring Wires